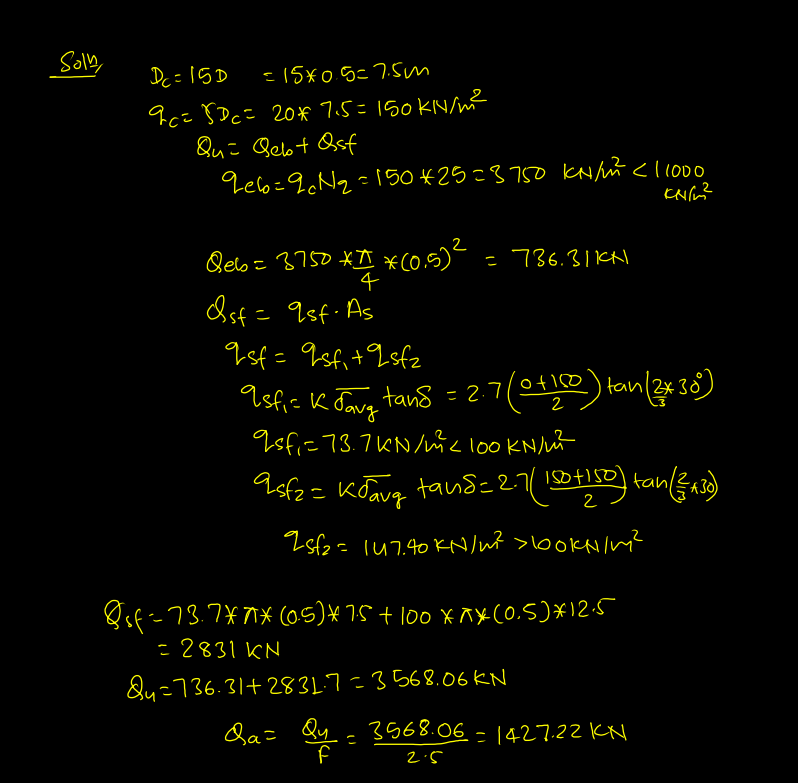In situations where the soil is poor at shallow depth, in such case safely transfer the load at suitable depth deep foundation are provided. These are further classified as piles, pier & well foundation.
Piles can be classified on the basis of following :
On Basis of material used for construction
- Timber pile
- Concrete Pile
- Steel Pile
- Composite Pile (Steel + timber)
On Basis of Cross Section
- Circular Pile
- Square Pile
- Hexagonal Pile
- I-Section Pile
- H-Section Pile
On the basis of shape
- Cylindrical Pile
- Tapered Pile
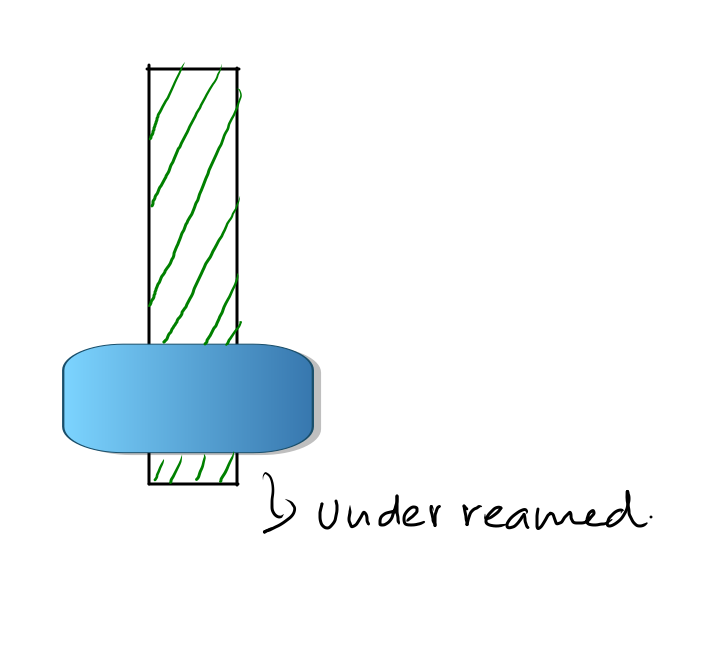
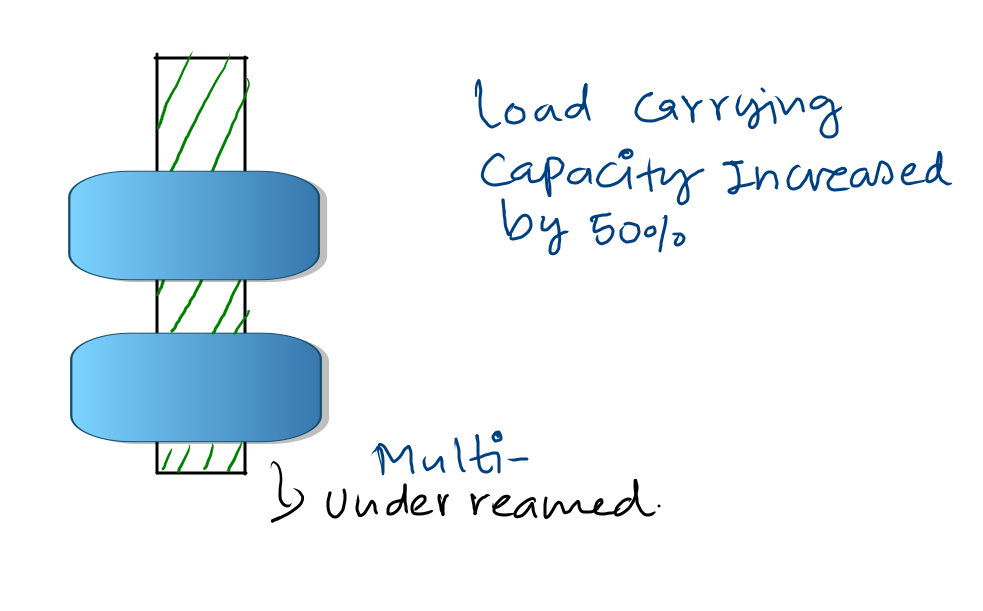
- Under-reamed pile
Mode of load Transfer
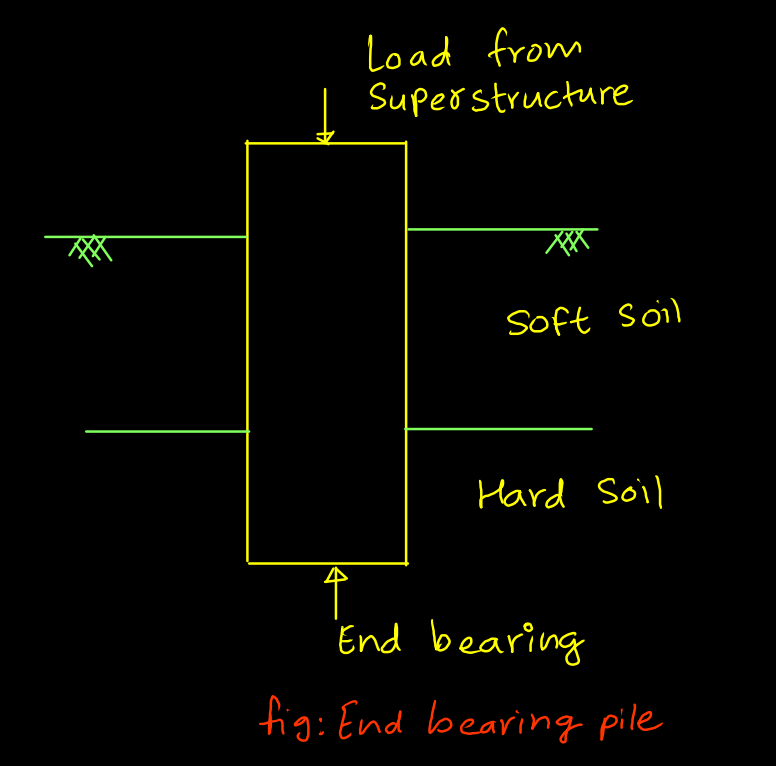
- End bearing Pile :- Pile which rest over hard strata. Length of this pile depends on the depth of hard strata meets.
2. Friction/Floating Pile/Hanging Pile :- Driven the soft clay or loose sand. Extremely length is higher than end bearing pile. Load resisting because of side resistance/friction. Load transfer through skin friction.
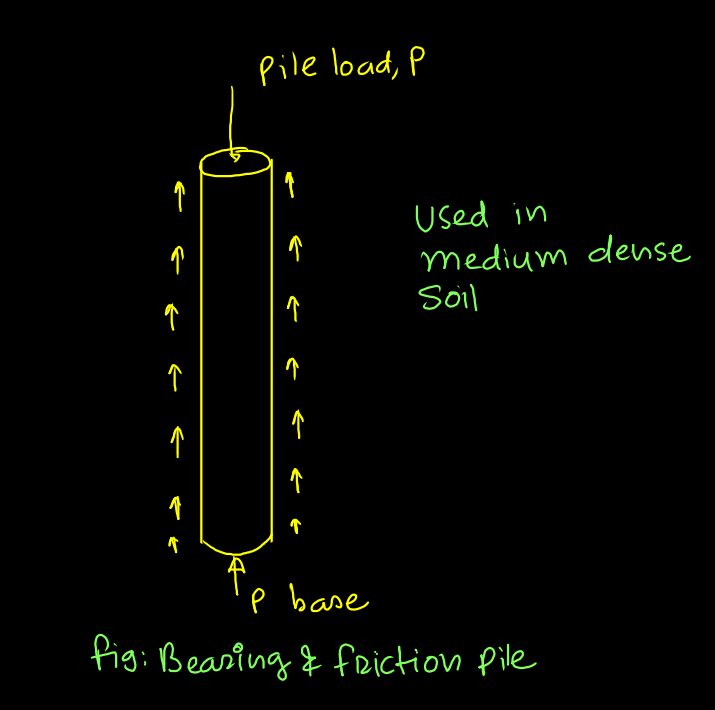
3. Bearing and Friction Pile:- It is combination of both.
On the basis of forming
- Precast pile
- Cast in situ pile
- Prestressed Pile
On the basis of function
- Laterally Loaded Pile (Abutment & bridge)
- Batter Pile (Batter means Inclination, it is for Large lateral load )
- Tension Piles (When the load is upward direction i.e. uplift load, provided in expansive soil to resist uplift load)
- Anchor Piles (Provides anchorage against horizontal pull)
- Sheet Pile (Retainment to the earth fill to avoid from seepage)
- Fender Pile (Marine structure against floating agent)
On the basis of installation of pile on soil
- Displacement Pile/Driven pile
- Non-Displacement Pile
It is based on following :
- Type of soil & location of water table
- Type of structure & Load
- Location (loose, sea, hard strata, non-hard strata)
- Cost
Load carrying capacity of pile can be computed by any of the following method:
- Static/Analytical Method
- Dynamic method/Pile Driving Method
- Pile Load Test Method
- Correlation with penetration test
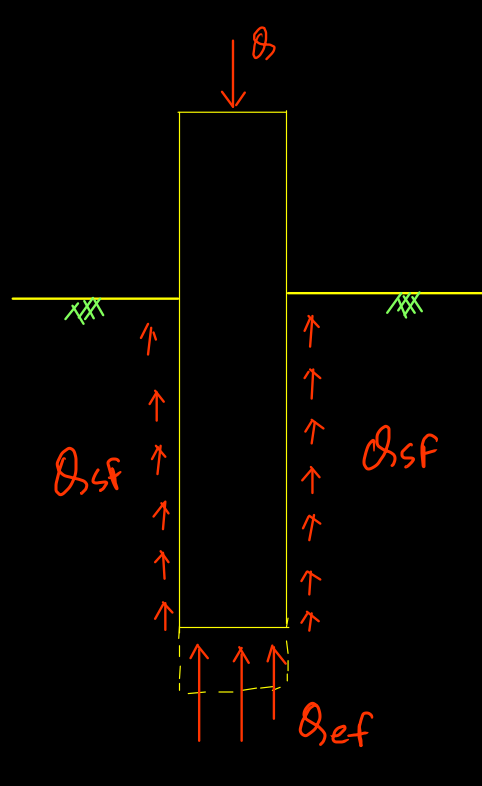
When the load is applied in the pile, friction develops. As the load increase the friction develop throughout the length of pile is termed as ultimate friction resistant. if the load increment more than ultimate skin friction, load transfer to the base of pile and resist by bearing resistant. Until the ultimate skin friction develop, end bearing is equal to zero. When end bearing friction develops, skin friction reduces.

Load resistant by skin friction and end bearing dependent on shear strength of soil.
Ultimate skin friction develop depends on load on pile

Case 1. Cohesive Soil :
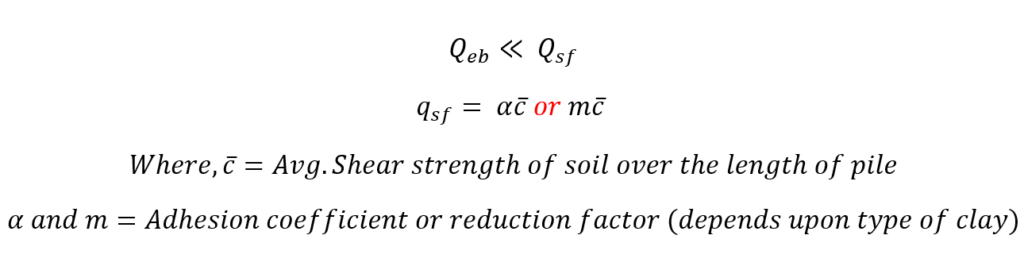
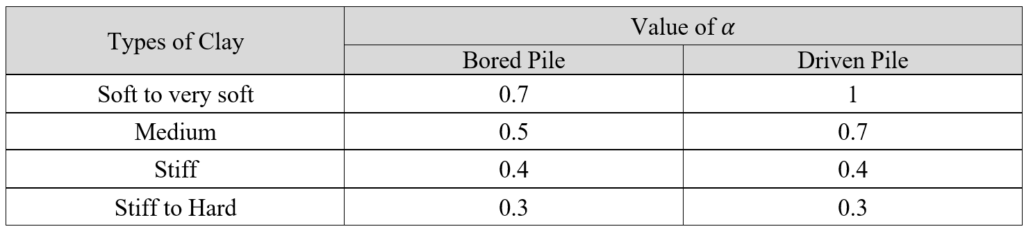
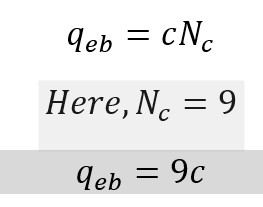
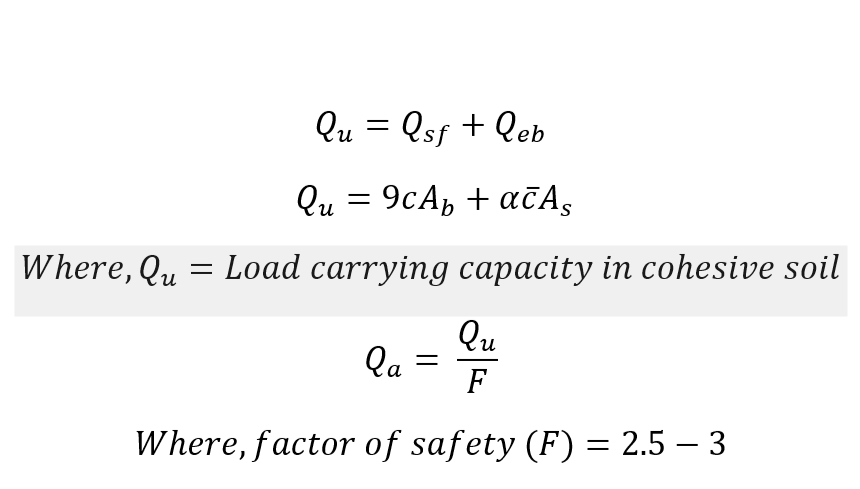

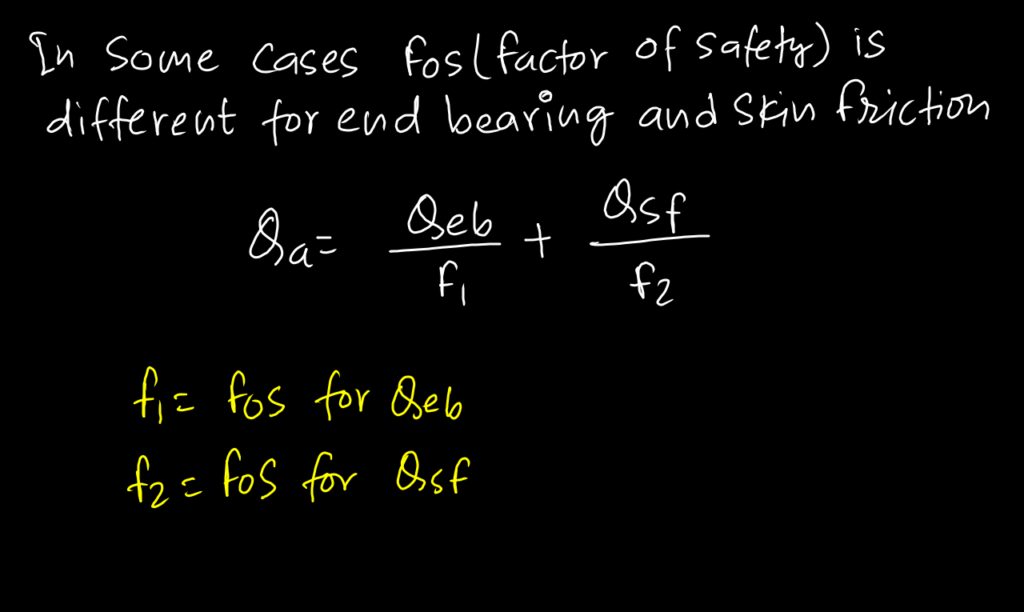
Case 2. Cohesionless Soil :
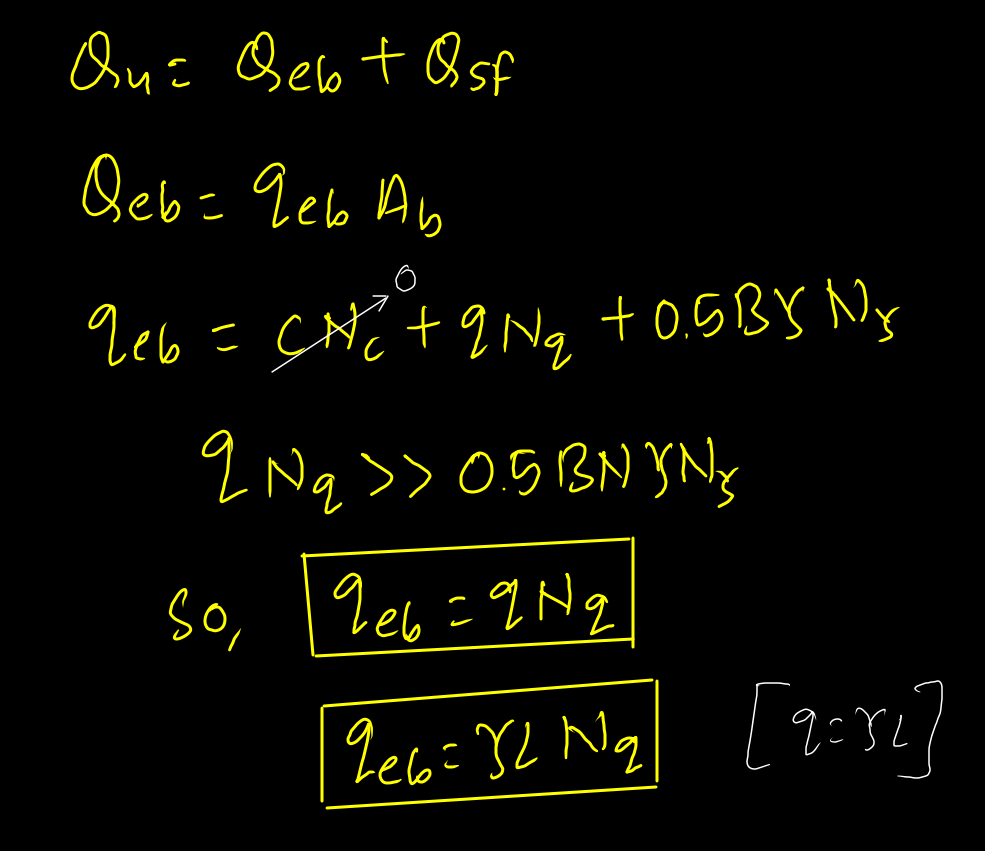
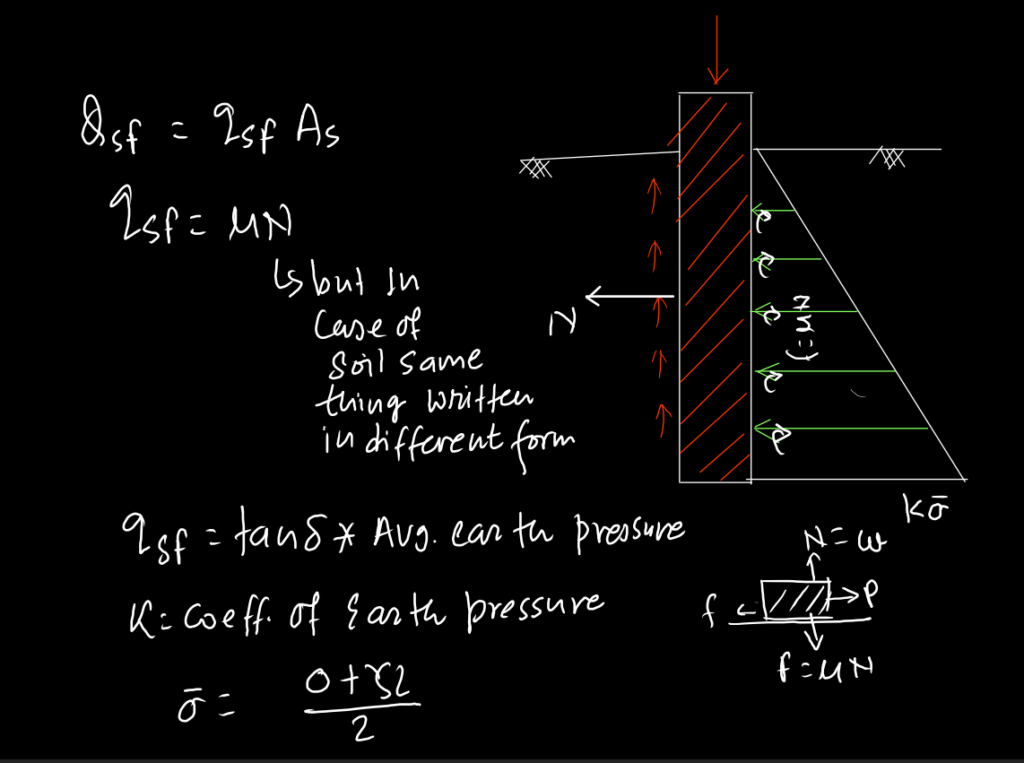

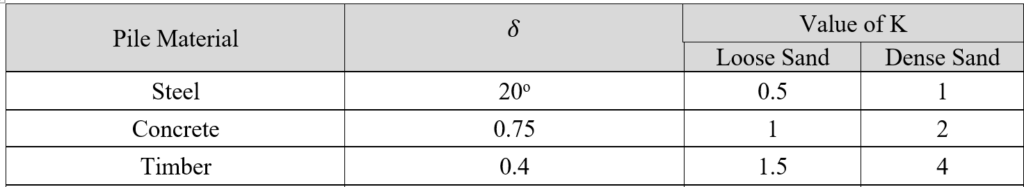



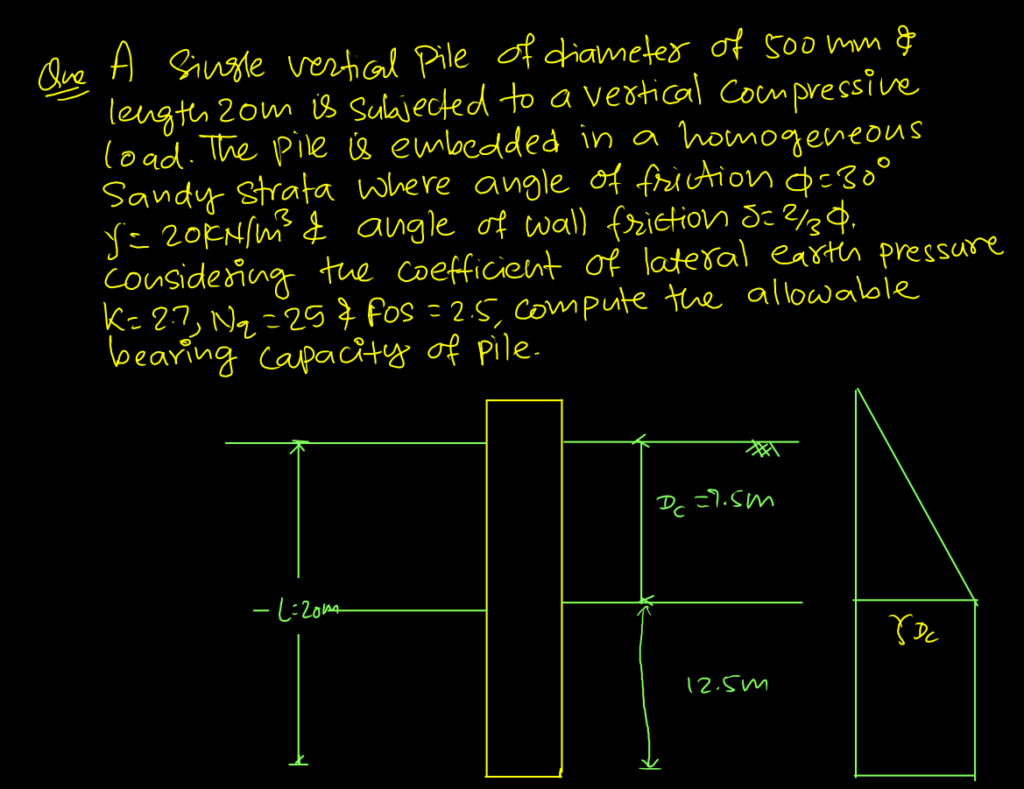
From the above relationship, it is concluded that qeb increases linearly with depth of pile but in actual, it increases upto a particular depth (critical depth) beyond which its remain constant. This is due to Arch Effect in granular soil. Critical depth in range (15-20)D, where D=Diameter of pile.
- 15D for loose to medium sand
- 20D for dense sand
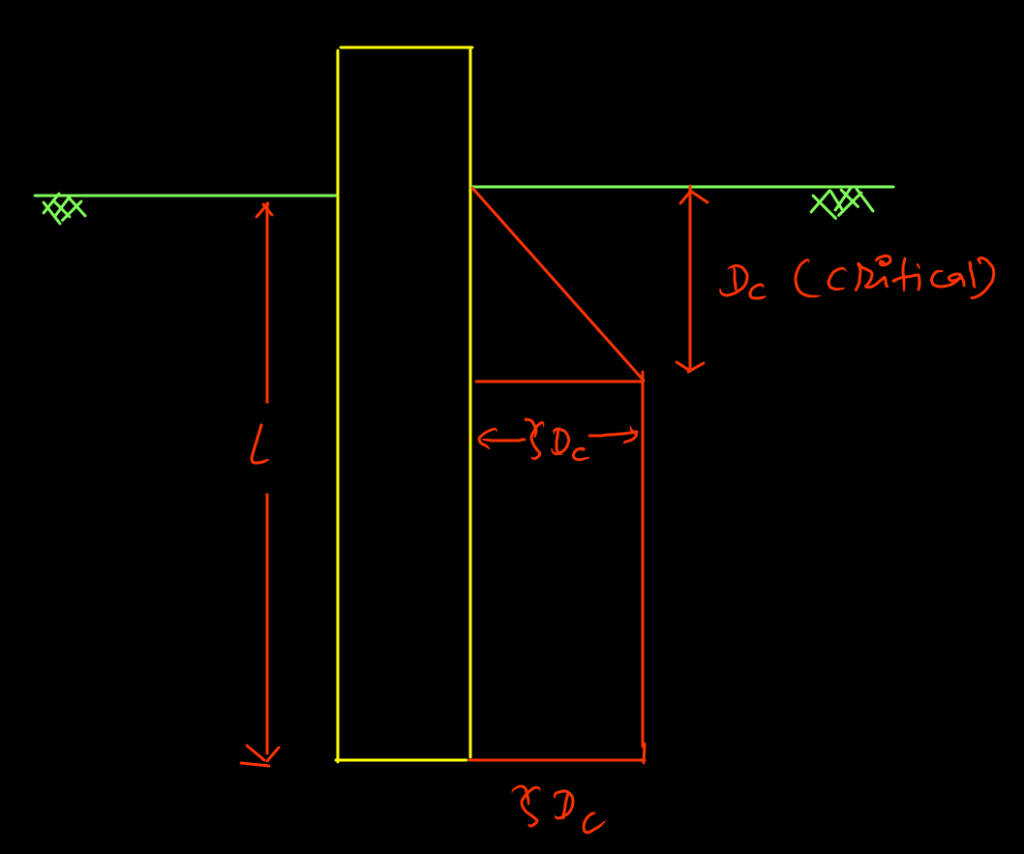
Maximum value of unit end bearing resistance is also limited.
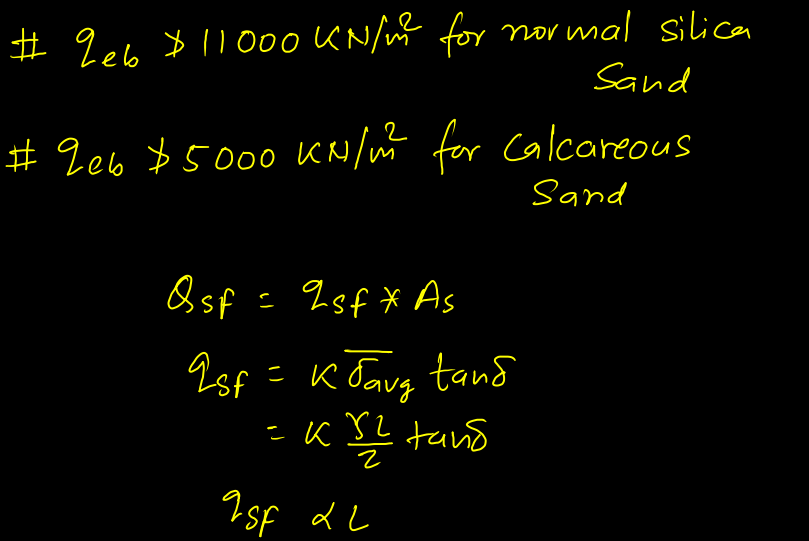
From above relationship, it can be concluded that qsf increases with length of pile but in actual it happens only upto critical depth, beyond which it becomes constant.