Manufacturing of concrete is carried out in sequence order as follows:
It is the process of measuring the ingredients required for preparation of the concrete. It can be done by volume and by weight.
Batching by volume is not preferred if it is applied the correction of buckling is to be applied. Volume of batching is generally avoided as correction due to bulking to be applied in this case. It can be adopted for minor engineering work only after permission of engineer in-charge. Tolerance permitted is measurement as per IS 4925 (Code for batching only)
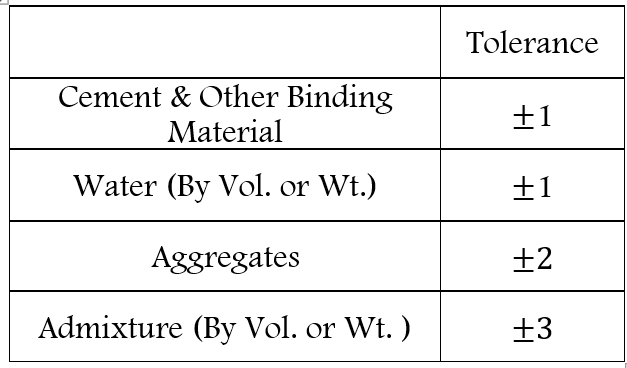
Water is always measured in kg or litre and cement is always measured by weight irrespective of method of batching.
The objective of mixing is to obtain homogeneous & uniform colour concrete of desirable strength. Mixing time depends on capacity of mixture. IS456 suggests the mixing time to be 2 min. Generally, 20 revolutions of mixer are sufficient to be obtain desirable mixing. Mixing can be done any of the following method.
- Hand Mixing (10% more cement use than machine mixing)
- Machine Mixing :- It is two types : Batch type (Tilting type) and Continuous Type (Non-Tilting type)
The process of carrying the concrete to desired point of application is termed as transportation. The entire process of mixing, transporting, placing, compacting and finishing must be completed in less than initial setting time of cement (30 min).
Transportation of concrete can be done by any of the following methods:
- Pan : Locally used where less distance to transport.
- Hand buggies : Use where less distance and transport in high speed.
- Power Buggies : More distance and high speed.
- Crane bucket : Used in vertical plan, less horizontal plan.
- Dump Truck: It is used in under ground level.
- Chutes : Under ground level.
- Transit Mixer: Used in congested area.
- Belt Conveyor : Mostly Used for large quantity to transport.
- Tower Bucket : Used in high horizontal plan than vertical plan.
- Tremie: For more depth.
- Concrete Pumps: To provide energy to concrete.
The process of application of concrete at desired location is termed as placing.
The process of removal of entrapped air from the void of concrete in order to obtain uniform placement & to form homogeneous dense mass is termed as compaction. In context of air in concrete, it can be classified into two types
- Entrapped air (10-1000μ) : Non Uniformly Present
- Entrained air (5-80μ): Uniformly Present
Note : If air entrapped, efficiency of concrete is reduced by 30-40% therefore compaction is necessary to do.
Compaction of concrete can be done by any of the following method:
- Hand Rodding
- High Pressure/Shock
- Centrifugation/Spining
- Mechanical Vibration (Immersion/Needle Vibrations, Surface Vibration, Plane table vibration, External/Shutter vibrators)
As Per IS456 It is the process of preventing the loss of moisture from the concrete required for hydration & to maintain satisfactory temperature regime. It must be done at least for 3 weeks & in no case must be less than 10 days. It is done at temperature 5-28oC & humidity of 90%.
In first three weeks C3S also hydrated, and high water losses result decrease in strength, for that purpose also curing is crucial.
Curing can be done any of the following Method:
- Shading
- Covering with sunny bags
- Sprinkling Water
- Ponding with Water
- Application of curing Compounds (Bitumen, Wax, Acrylates, Chlorinated, rubber, sodium silicate (water glass).
- Accelerated Curing (Stem/Infrared Rays)
Drawback of accelerated curing : It decrease shear strength of concrete because rate of vibration increased perfect binding not takes place.
It is defined as process of levelling or smoothing of top surface of freshly placed concrete to achieve the desired appearance.


