It is a structural member of which one dimension is very small as compared to other two dimensions. It is primarly subjected to bending. Slab can be classified on the basis of following:
a) On the basis of the shape
- Rectangular
- Circular
- Triangular
- Any other shape
b) On the basis of Bending Behavior
- One way Slab
- Two Way slab
c) On the basis of type of construction
- Slab/Solids Slab
- Flat Slabs
- Slab with opening
- Waffled Slab
d) On the basis of type of loading
- Slab subjected to Point Load
- Slab subjected to UDL
Note: Analysis and design solid, rectangular one way & two way slab subjected to UDL will be considered.
If bending in one direction is very significance than other orthogonal direction then the slab is termed as one way slab.
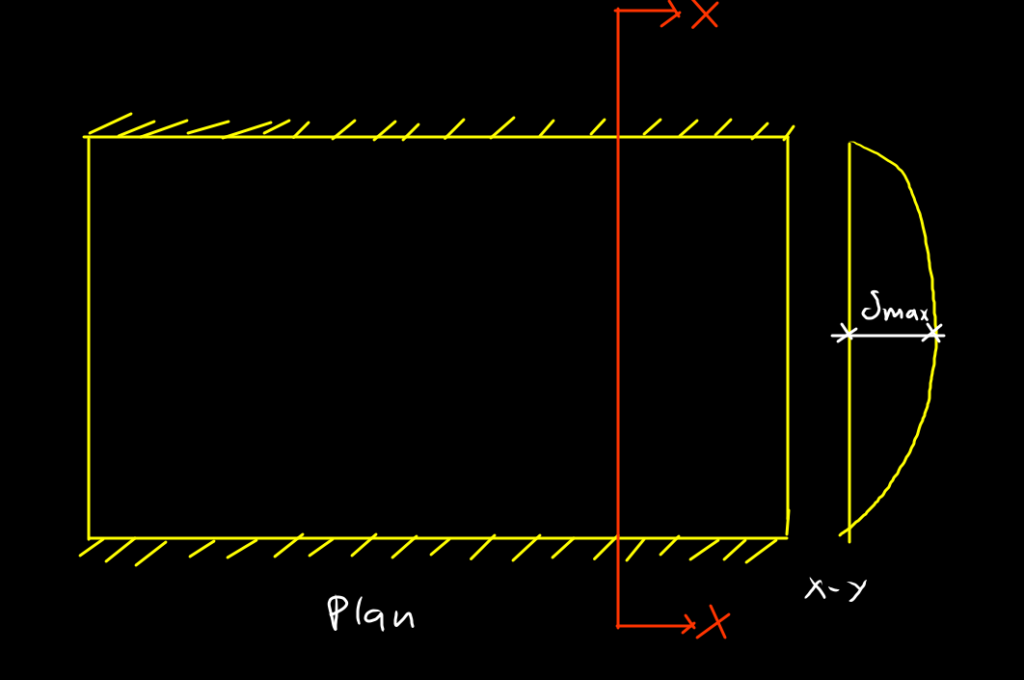
a) Rectangular slab supported from opposite edges (it always one-way slab irrespective of dimensions)
b) Rectangular slab supported from all four edges.
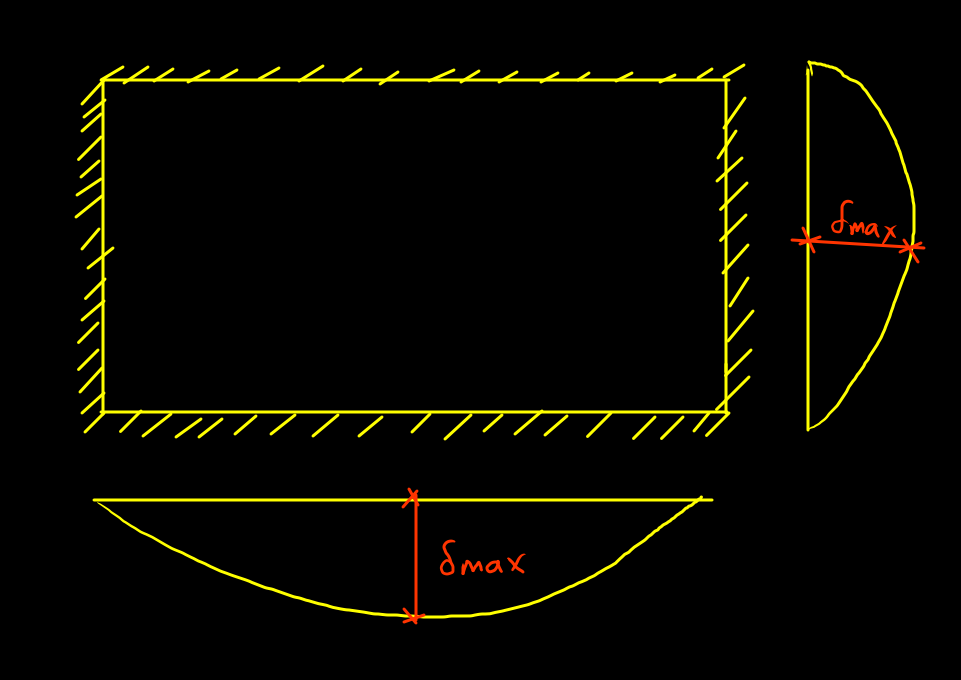
Aspect ratio is defined when all edges are supported.
It can be one way slab if aspect ratio is greater than 2.
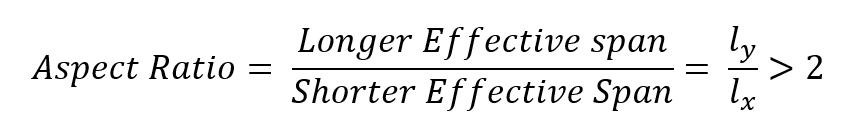
Note : Aspect ratio valid only for rectangular slab supported on four sides.
If bending is comparable in two orthogonal directions such slab is termed as two way slab. If Aspect ratio < 2 and rectangular slab is supported from all sides then it is termed as two way slab.
It is slab that directly rest on column. Sometimes drops panels or column capital are also used to prevent punching failure of these slabs as they behave like two way slab. Its thickness is invariably higher than solid slab but still it is provided as,
- For better aesthetic appearance.
- For better Dispersion of height
- For ease in providing ducts.
- It offers lesser storey height.
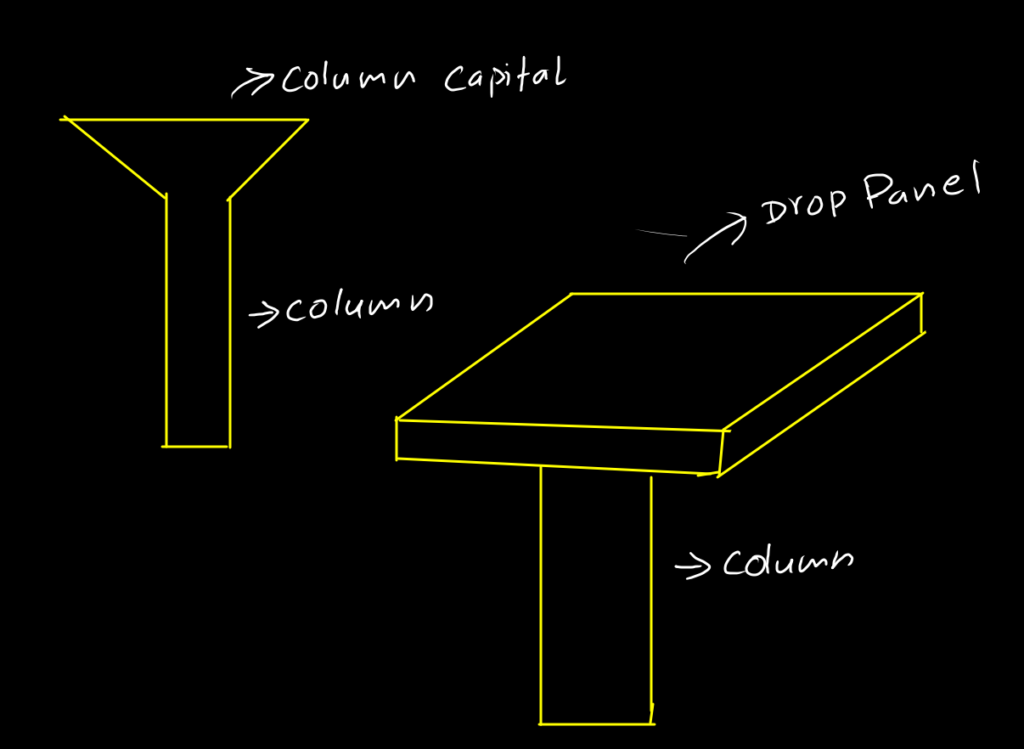
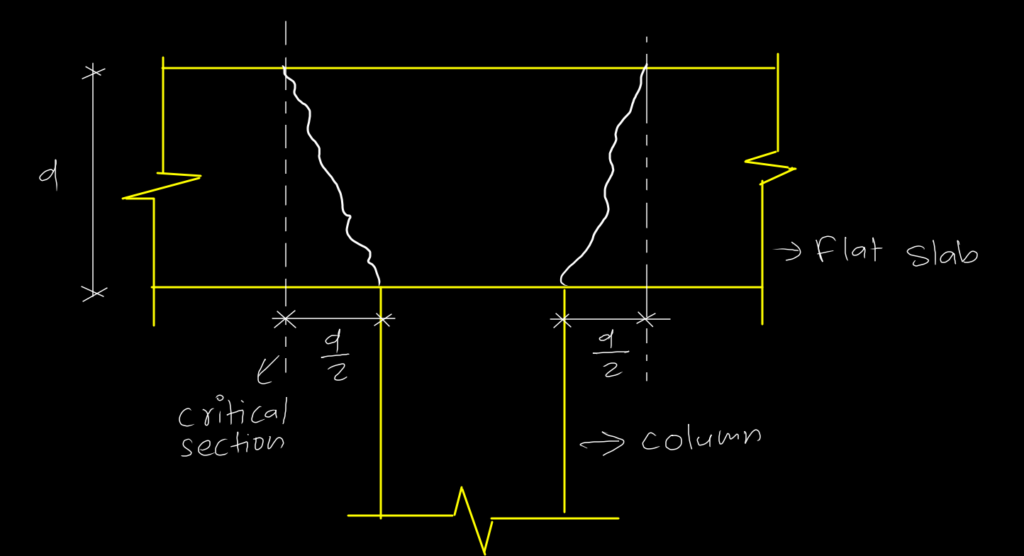
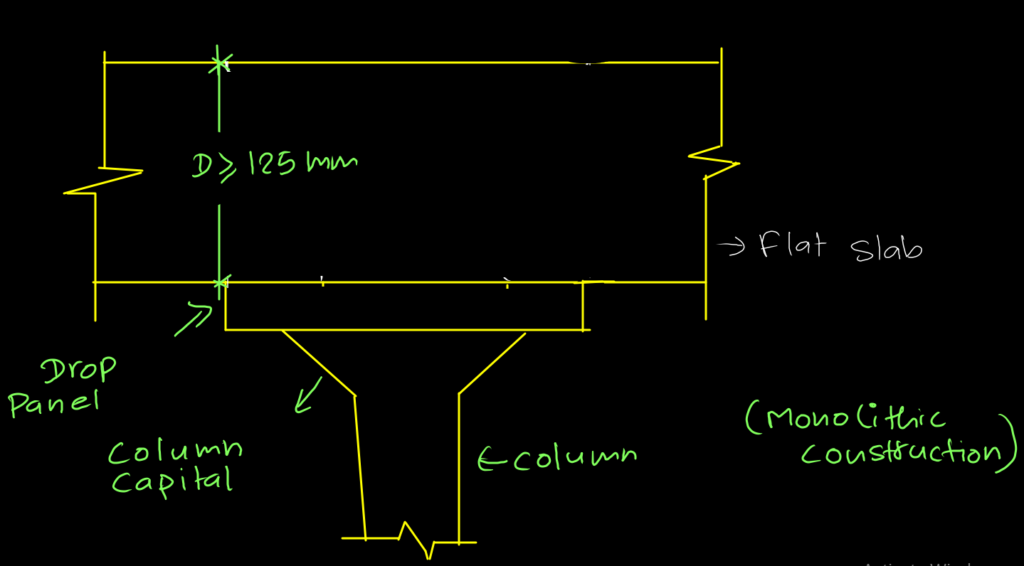
Purpose of drop panel or column capital is to reduces stress.


